Preloader Close
Stroke & Cerebrovascular Lesions
- Home
- Stroke & Cerebrovascular Lesions
Stroke & Cerebrovascular Lesions
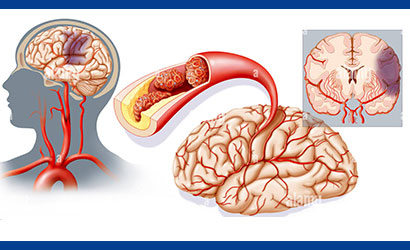
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted or reduced, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients, leading to cell damage. Cerebrovascular lesions refer to abnormalities in the blood vessels of the brain, such as aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), and small vessel disease, which can increase the risk of stroke.
Causes of Stroke & Cerebrovascular Lesions
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Atherosclerosis (narrowing of blood vessels due to plaque buildup)
- Blood clots or embolism
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Obesity and sedentary lifestyle
- Heart disease (such as atrial fibrillation)
- Genetic predisposition
Symptoms of Stroke
- Sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg (especially on one side)
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Blurred or double vision
- Loss of balance or coordination
- Severe headache without a known cause
- Dizziness or confusion
- Loss of balance and coordination
Treatments
Emergency Treatments for Stroke
- Intravenous Thrombolysis (tPA): A clot-busting drug administered within the first few hours of an ischemic stroke.
- Mechanical Thrombectomy: High-energy beams to shrink or destroy cancer cells
- Chemotherapy: A procedure to remove a blood clot using a catheter.
Long-Term Management & Rehabilitation
- Medications: Blood thinners, antihypertensives, and cholesterol-lowering drugs to prevent future strokes.
- Physical Therapy: Helps regain muscle strength and coordination.
- Speech Therapy: Assists in recovering communication skills.
- Occupational Therapy: Helps restore daily functional abilities.
Surgical Treatments for Cerebrovascular Lesions
- Carotid Endarterectomy: Surgery to remove plaque from carotid arteries.
- Aneurysm Clipping or Coiling: Procedures to treat aneurysms and prevent rupture.
- Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) Treatment: Surgery or embolization to prevent brain bleeding.
Prevention of Stroke & Cerebrovascular Lesions
While brain tumors cannot always be prevented, certain lifestyle habits can help lower the risk:
- Control Blood Pressure: Maintain a healthy blood pressure through lifestyle changes and medication.
- Eat a Healthy Diet: Low in saturated fats, salt, and cholesterol, and rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise daily.
- Quit Smoking & Limit Alcohol: Reduces the risk of vascular damage.
- Manage Diabetes & Cholesterol Levels: Helps prevent arterial blockages.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Early detection of risk factors can prevent stroke.
