Preloader Close
Nerve Entrapment Syndrome
- Home
- Nerve Entrapment Syndrome
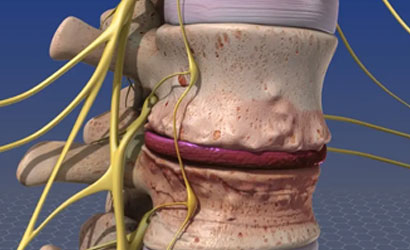
Nerve Entrapment Syndrome
Nerve Entrapment Syndrome occurs when a nerve is compressed or irritated due to surrounding structures such as bones, muscles, tendons, or ligaments. This compression can lead to pain, numbness, weakness, or tingling sensations in the affected area.
Common Types of Nerve Entrapment Syndromes:
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Compression of the median nerve in the wrist, causing pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and fingers.
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome: Compression of the tibial nerve in the ankle, leading to foot pain, burning sensations, and tingling.
- Peripheral Nerve Entrapment Syndrome: Involves compression of peripheral nerves in various parts of the body, causing discomfort and functional limitations.
Causes of Nerve Entrapment Syndrome
- Repetitive motions (e.g., typing, manual labor)
- Prolonged pressure on nerves
- Injuries or trauma
- Inflammatory conditions like arthritis
- Obesity or excessive weight gain
- Diabetes-related nerve damage
Symptoms
- Pain or discomfort in the affected area
- Tingling or numbness
- Muscle weakness
- Burning sensation
- Reduced mobility or difficulty in movement
Treatment Options
Non-Surgical Treatments:
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening and stretching exercises to relieve pressure.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs and pain relievers.
- Bracing or Splinting: Supports to keep the affected area stable.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Ergonomic adjustments, weight management, and avoiding repetitive movements.
- Nerve Gliding Exercises: Helps in reducing nerve irritation.
Surgical Treatments (If Necessary):
- Carpal Tunnel Release: Surgery to relieve pressure on the median nerve.
- Tarsal Tunnel Release: Procedure to relieve tibial nerve compression.
- Decompression Surgery: Used for severe cases where non-surgical methods do not provide relief.
Prevention:
- Maintain proper posture while working.
- Take frequent breaks from repetitive activities.
- Use ergonomic equipment to reduce strain.
- Exercise regularly to keep muscles flexible and strong.
- Manage underlying health conditions like diabetes and arthritis.
